System-on-Chip
Full chip implementation for computer vision and machine learning
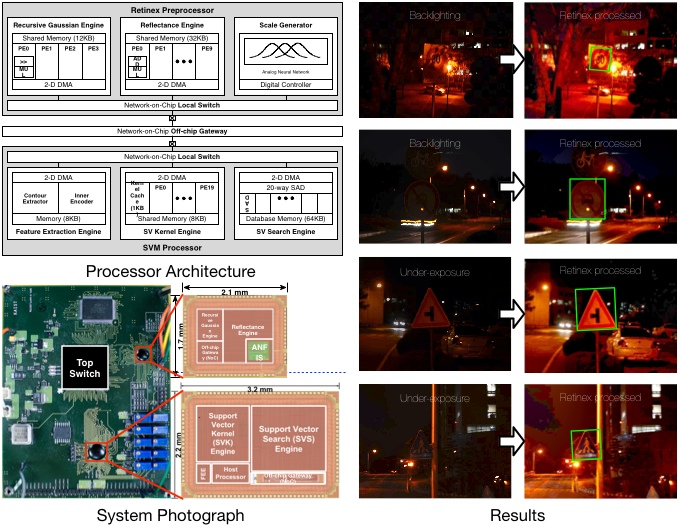
Traffic Sign Recognition Processor
We propose a robust real-time traffic sign recognition system with two-chip integration: a Retinex preprocessor and a SVM processor. The Retinex preprocessor performs the Multi-Scale Retinex (MSR) algorithm for robust light and dark adaptation under harsh illumination environment. The SVM processor performs the Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm for robust traffic sign classification. The proposed system is implemented as two separated ICs in a 0.13μm CMOS process and the two chips are connected using Network-on-Chip (NoC) off-chip gateway.
Relevant Paper:
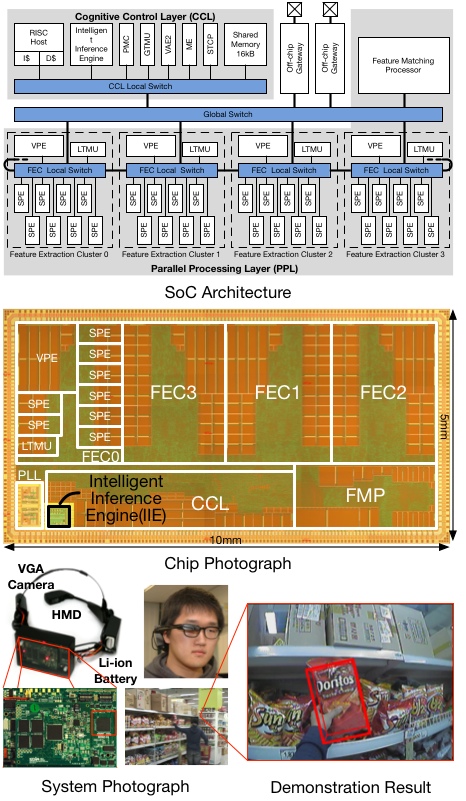
Many-core Object Recognition Processor for Augmented Reality Headset
Augmented reality has recently been gaining popularity in the consumer sector, especially in the form of smart phone apps. However, the actually useful apps are still limited to GPS based navigation applications, in which information about stationary locations and/or movement directions are overlaid on top of a phone’s camera input video. Vision based augmented reality has the potential for much more useful and entertaining applications such as games involving interaction with real world objects, and more realistic overlays that blend in with the environment. However, until now, the limited performance of mobile hardware has been an obstacle to realizing real-time object recognition needed by such applications. The main requirements for real-time vision based augmented reality in a mobile form factor are high performance, and low power.
In this work, we presented an object recognition processor aimed at real-time vision based augmented reality in mobile applications, which achieves high performance yet low power operation by employing a heterogeneous array of simple processors. Multiple stages of processing, common to modern local feature based object recognition algorithms, plus an additional pre-processing stage for visual attention are pipelined using these optimized programmable processors to achieve 30fps real-time performance on VGA video streams. The object recognition chip, containing 51 IPs in two voltage/frequency domains, was fabricated in a 0.13 µm CMOS process, and verified to operate at 1.2V/200MHz and 0.65V/50MHz.
In the demonstration system, the object recognition chip successfully recognizes pre-learned objects that are saved in the database at a rate of 30fps from VGA video images. Tests carried out in indoor/outdoor environments verify the robustness of the object recognition chip, and the viability of vision based augmented reality systems in a mobile form factor.
Relevant Paper:
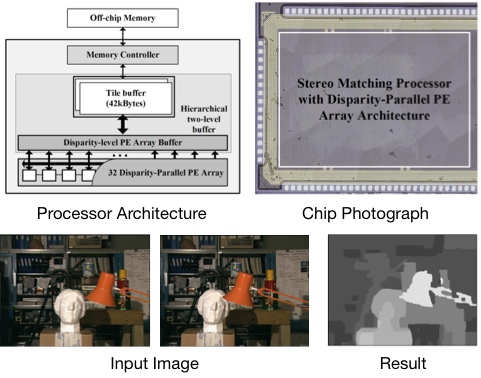
Belief Propagation based Stereo Matching Processor
A real-time stereo matching processor based on the belief propagation algorithm has been designed. We propose a disparity-parallel PE array architecture for computationally complex message construction. Also, we adopt a tile-based belief propagation approach reduces the on-chip memory requirements. In addition, a two-level on-chip buffer and memory access pipelining enable high PE utilization. As a result, the message construction rate of the PEs is increased by 6.45x compared to previous works. The fabricated processor in a 0.18um CMOS process achieves 30 fps performance for QVGA (320x240) video inputs at 200 MHz operating frequency.
Relevant Paper:
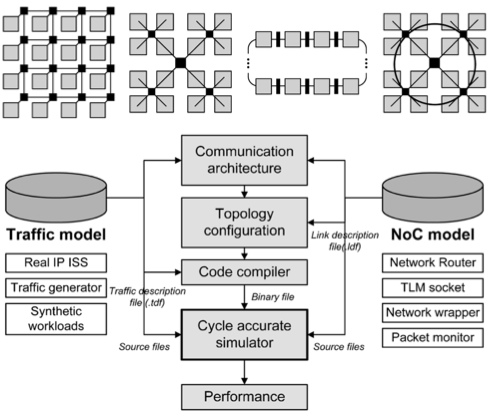
Network-on-Chip
System-C based cycle-accurate architecture simulation
A Multi-Casting Network-on-Chip with Hierarchical Star-Ring Combined Topology
A multi-casting network-on-chip has been proposed as communication platform for a real-time object recognition. In this work, I have implemented a cycle-accurate Network-on-Chip architecture simulator using System-C libraries with TLM socket interface, and the traffic model libraries. The traffic model library contains synthetic traffic patterns and traffic generating subjects such as real IP's instruction set simulator and traffic generator. Using the implemented NoC simulator, we measured the average latency, bandwidth utilization, and implementation cost of several NoC topologies when the object recognition runs for VGA images. As a result, we have drawn a conclusion that the HS-R combined topology is suitable for the communication platform in real-time object recognition.
Relevant Paper: